Optimizing Big Data Workflows

Data-Driven Healthcare: Transforming Patient Outcomes
In the current data driven world, the ability to grasp, interpret, and use data has become an essential skill in every field. Right from healthcare to finance, technology to education, data literacy is no longer just a luxury; it’s an essential requirement for success. Workforce empowerment and organizational success depend on data literacy, which is the ability to understand, evaluate, and analytically make wise judgments from information.
As businesses leverage on big data and analytics, the importance of creating a knowledgeable workforce becomes more and more relevant.
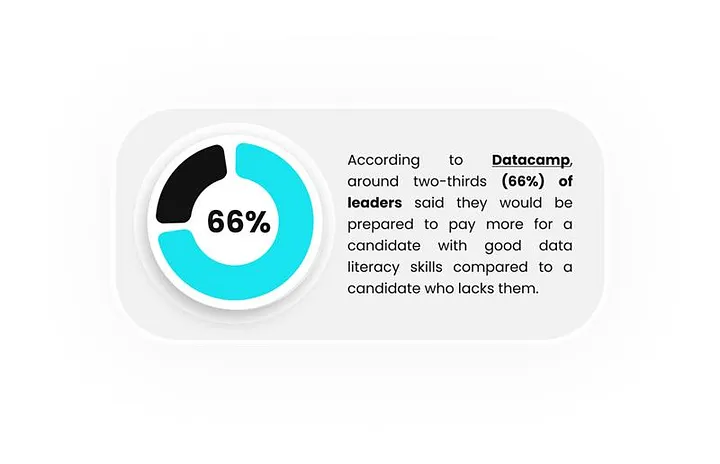
According to Datacamp, around two-thirds (66%) of leaders said they would be prepared to pay more for a candidate with good data literacy skills compared to a candidate who lacks them, with 77% of yes responders saying they would pay 10% to 15% more. Around a quarter of leaders would provide a 30% salary premium or more for candidates with good data literacy skills.
DataCamp
Further, we will explore the concept of data literacy, its importance in modern workplaces, the key components of a data-literate organization, and strategies for empowering employees with the necessary skills.
Data Literacy: A Brief Introduction
Data literacy refers to the ability to read, work with, analyze, and communicate with data effectively. It includes a wide range of skills, such as:
Understanding kinds and sources of data
Understanding data visual representations
Analyzing data and finding insights.
Making data-based decisions.
Effective explanation of results and advice from research.
Every employee, irrespective of their position, should have a basic level of data literacy to help their company to be successful. Hence, it should not be only limited to data scientists or analysts.
The Importance of Data Literacy
1. Enhanced Decision-Making:
Good data analysis is the basis of informed decision-making. Data literate employees can analyze information well, therefore increasing the quality of strategic decisions driving company growth.
2. Increased Efficiency:
Data literate staff can identify patterns and anomalies fast, thus they can simplify operations and cut waste. This effectiveness results in cost savings and higher output.
3. Competitive Advantage:
Companies valuing data literacy enable their staff to engage use data insights in creativity. In today’s competitive world, the power to act on data can give quite an edge to businesses in the market.
4. Fostering a Data-Driven Culture:
Developing data literacy helps to create a culture of data driven decision-making throughout every level of an enterprise. Using data in their daily operations is something employees who are trained to work with data will more likely do.
5. Employee Empowerment:
Providing staff with data capabilities helps to increase confidence and inspires them to be in charge of their work. Empowered employees are motivated and more involved in work.
The Components of Data Literacy
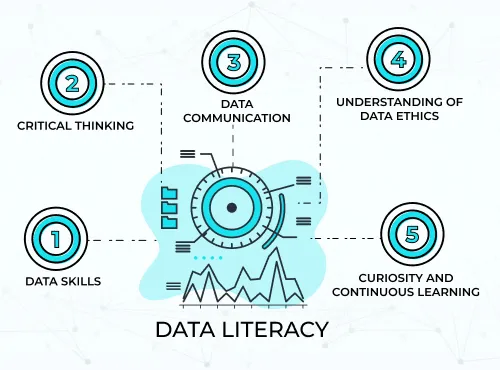
1. Data Skills:
Including data collection, cleansing, analysis, and visualization, which covers data abilities. Data visualization tools such Tableau or Power BI as well as Excel, SQL, and other tools utilization for data analysis should be mastered by employees.
2. Critical Thinking:
Being data literate means having a critical thinking attitude. Before drawing conclusions, staff members should be capable of questioning data sources, challenging premises, and appraising data accuracy.
3. Data Communication:
Effective data insights communication is critical. Using suitable graphics to back their points, employees should be able to communicate their results to peers and stakeholders in coherent and understandable language.
4. Understanding of Data Ethics:
Great data requires great responsibility. The workforce should understand the ethical issues related to data usage, including bias in data, privacy laws, and data governance policies.
5. Curiosity and Continuous Learning:
Data literate employees help to promote a culture of curiosity and continuous learning. Employees should be interested in trying different data tools and techniques meant to help them to keep up with changing data environments.
The Components of Data Literacy
How to Build Data Literacy in the Workforce?
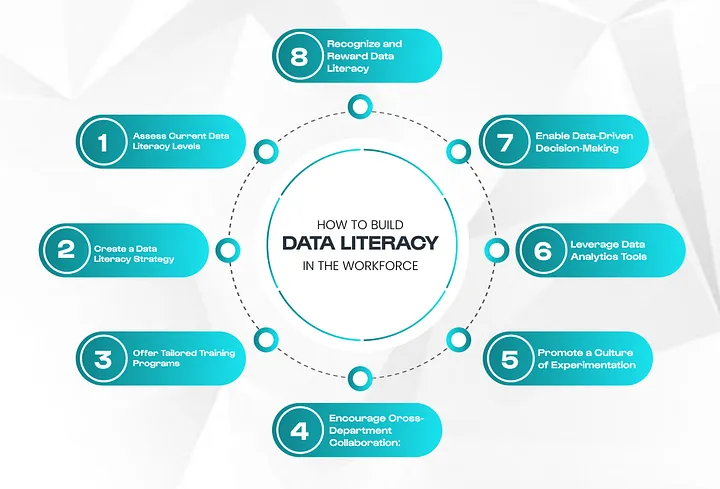
1. Assess Current Data Literacy Levels:
Start by appraising the present data literacy rates in your business. Do evaluations or polls to find areas for improvement and strengths.
2. Create a Data Literacy Strategy:
Develop a data literacy plan that fits with the objectives of your company so as to help you there. Your plan should clearly state goals, training courses, and the tools needed for their accomplishment.
3. Offer Tailored Training Programs:
Develop training programs personalized to the many positions within your company. While some staff members may need sophisticated data analysis abilities, others may only need simple data interpretation abilities. Consider:
Workshops and Seminars: Host hands-on workshops on basic data literacy ideas and techniques.
Online Learning Platforms: Make use of online courses or websites offering data literacy training aimed at different skill levels.
Mentorship Programs: Pair more experienced workers with data savvy mentors to provide direction and individual support.
4. Encourage Cross-Department Collaboration:
Develop collaboration among departments to distribute information. Developing cross functional groups might help for knowledge exchange and group learning.
5. Promote a Culture of Experimentation:
Help staff members in a secure setting to try data analysis. Give opportunities to employees to try new tools and approaches free of concerns of failure.
6. Leverage Data Analytics Tools:
Encourage employees with easy data analytics tools that streamline data analysis. These instruments let staff members see data without the need for much technical expertise.
7. Enable Data-Driven Decision-Making:
Strengthen data driven decision-making at every level of organization. Empower staff to support their ideas with data, therefore cultivating ownership and accountability.
8. Recognize and Reward Data Literacy:
Acknowledge employees who display excellent data literacy and offer valuable data knowledge. Recognition and incentives can inspire people to better their abilities still more.
Data Literacy in the Workforce
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Data Literacy Programs
In the current business landscape, data literacy — the capability to read, interpret, produce, and transmit data as information — has grown to be an essential skill. Businesses in different disciplines are investing in data literacy initiatives to support better decision making, increase efficiency, and foster a data driven culture. Below are two real life case studies illustrating effective use of data literacy.
Case Study 1: Healthcare Company Enhances Data-Driven Decision-Making
Company: Novartis (Global Pharmaceutical Firm)
Challenge:
Novartis, a global leader in the pharmaceutical industry, recognized a growing challenge: employees at all levels lacked the necessary data literacy skills to make data-informed decisions. As a result, critical insights from vast healthcare datasets were underutilized, limiting the organization’s ability to optimize patient outcomes, streamline operations, and drive innovation.
Novartis, a top pharmaceutical company worldwide, discovered a developing issue: workers at every level were lacking the data literacy needed to make informed decisions. Hence, the organization’s potential to streamline operations, drive innovation, and improve patient outcomes was limited by underused critical knowledge from extensive healthcare data sets.
Solution:
In response, Novartis initiated a corporate data literacy initiative intended to enable staff members with the abilities required to understand and apply information properly. The program comprised:
- Customized Learning Paths: Segmented by job titles and data abilities, employees were ensured personalized coaching.
- E-Learning & Hands-on Training: A mixture of self-paced classes, interactive seminars, and real-world data case studies
- Gamification & Certification: Employees were encouraged to participate via a tiered certification system.
- Data Champions: Selected staff members were trained as “Data Ambassadors” to boost team members and promote a culture centered on data.
Results:
- Improved Decision-Making: Employees grew more confident in analyzing patient data, sales reports, and clinical trial information.
- Faster Time-to-Market for Drugs: Novartis simplified R&D by using knowledge gained from better data literacy.
- Cost Savings: Department wide multimillion dollar savings were achieved from lower inefficiencies.
- Cultural Shift: Using data for strategic planning and creativity, employees nowadays actively interact with it (Source: Accenture).
Case Study 2: Financial Institution Builds a Data-Driven Workforce
Company: JPMorgan Chase & Co. (Leading Financial Services Firm)
Challenge:
One of the biggest worldwide financial companies, JPMorgan Chase, dealt with data silos and different degrees of data fluency among workforces. Lack of analytical and financial data interpretation among many staff members, especially those not in technical roles, resulted in inefficiency in investment strategies, fraud detection, and risk management.
Solution:
The firm launched the Data for All initiative, designed to create a solid data literacy foundation across functions. Major elements were:
- Company-Wide Data Training: Functions (HR to trading desks) employees engaged in interactive workshops.
- AI & Data Tool Familiarization: Personnel were given practical training on next-generation analytics tools such as Python, Tableau, and JPMorgan’s in-house AI models.
- Executive Buy-In & Leadership Involvement: Top executives strongly promoted data literacy, leading to widespread adoption across the company.
- Integration into Daily Operations: Workers implemented new skills in actual projects, solidifying learning.
Results:
- Increased Fraud Detection Efficiency: Employees were more able to identify fraudulent transactions through data analysis.
- Enhanced Customer Insights: Data-driven insights enhanced financial product personalization, leading to increased customer satisfaction.
- Higher ROI from Data Investments: Enhanced data literacy enabled teams to get the most out of AI and machine learning investments.
- Stronger Risk Management: Workforce made better-informed decisions about compliance and investment risk through the use of data (Source: Gartner).
Key Takeaways from Both Case Studies:
- Customized Training Yields Better Adoption: Both organizations adapted their initiatives based on employees’ roles and data abilities.
- Leadership Support is Crucial: In both instances, upper management was actively involved in advancing data literacy.
- Practical Applications Reinforce Learning: The workforce was inspired to use data abilities in actual business situations.
- Cultural Shifts Take Time but Deliver Long-Term Gains: Integration of data literacy in company culture resulted in long-term organizational benefits.
Through investing in data literacy, both JPMorgan Chase and Novartis revolutionized their workforces, resulting in enhanced efficiency, enhanced decision-making, and impactful business. These achievements can be learned from organizations in any industry to create their own data literacy initiatives.
Wrapping Up
Data literacy is a key skill in our current data environment, enabling employees to interpret and act on information from data insights. Through spending in data literacy initiatives, firms are able to instill culture of informed decision making, improve efficiency, and enhance overall performance.
Employees with data knowledge can effectively move through the landscape of data, which unlocks vast potential of enterprises, fuel innovation, and ultimately delivers business objectives. Data literacy is not only an investment in staff development but also a strategic necessity for organizations that want to succeed in the digital age.
As we move ahead in the data-driven age, it’s crucial for all organizations to rank data literacy highly. In the process, not only will they enable their workforce, but also set themselves up for long-term success in the ever-changing business landscape.
This Article also available here